Echocardiogram (Cardiac Ultrasound)
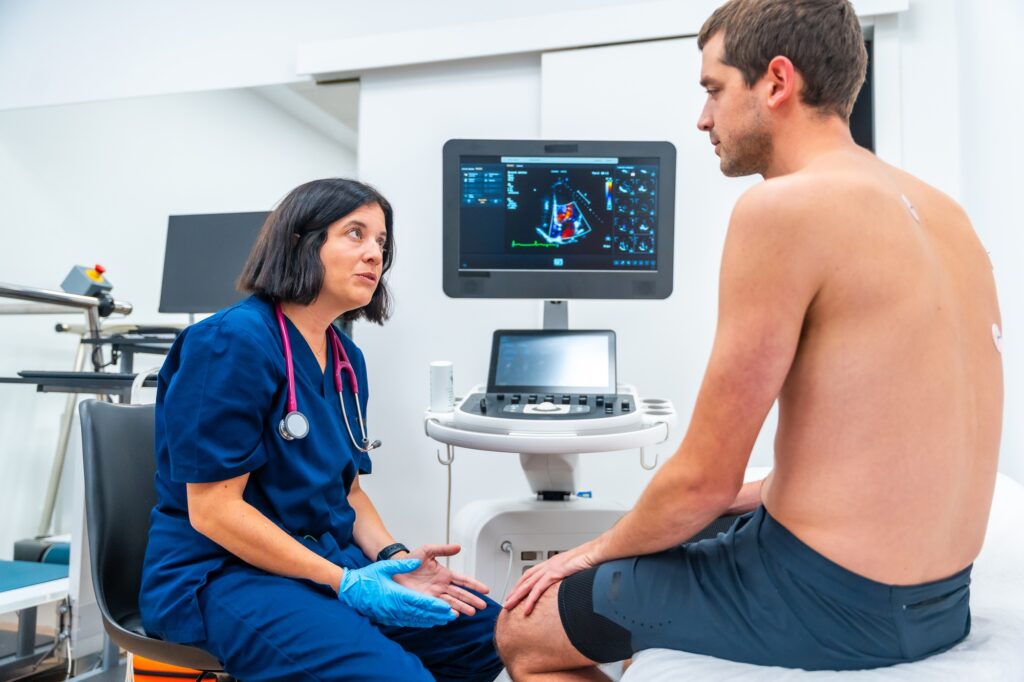
Purpose of an Echocardiogram
- Assess heart function: Examine how well the heart is pumping blood and the efficiency of its chambers and valves.
- Diagnose heart conditions: Detect issues such as heart valve disease, cardiomyopathy (heart muscle disease), heart failure, or congenital heart defects.
- Evaluate blood flow: Assess the flow of blood through the heart and identify areas of reduced or abnormal flow.
- Detect structural abnormalities: Identify issues like valve malfunctions, heart enlargement, or holes in the heart (such as in congenital conditions).
Types of Echocardiograms:
- Transthoracic Echocardiogram (TTE): The most common type, where the transducer is placed on the chest.
- Transesophageal Echocardiogram (TEE): In cases where clearer images are needed, a small, flexible tube with a transducer is passed down the esophagus, close to the heart. This is usually done under sedation.
- Stress Echocardiogram: This combines an echocardiogram with a stress test to assess how the heart functions under physical stress (usually after exercise or medication).

Benefits of an Echocardiogram
- Non-invasive: No needles, incisions, or surgery are involved. It is a painless test that does not require hospitalization.
- Real-time imaging: Provides live, moving images of the heart, allowing for an accurate assessment of heart function and blood flow.
- Accurate and detailed results: Helps detect a wide variety of heart conditions, even subtle issues that may not be apparent with other tests.
- No radiation: Unlike X-rays or CT scans, echocardiograms do not use radiation, making them safer, especially for pregnant women and children.
Who Should Consider an Echocardiogram?
- Are experiencing symptoms such as shortness of breath, chest pain, dizziness, or fatigue, which may indicate heart disease.
- Have a history of heart disease, including heart attacks, heart failure, or valve problems.
- Are being monitored for heart disease or conditions such as cardiomyopathy, congenital heart defects, or pericardial diseases.
- Need a pre-surgical evaluation to assess heart function before major surgery, especially for high-risk patients.

