Holter Monitor (Heart Rhythm Monitor)
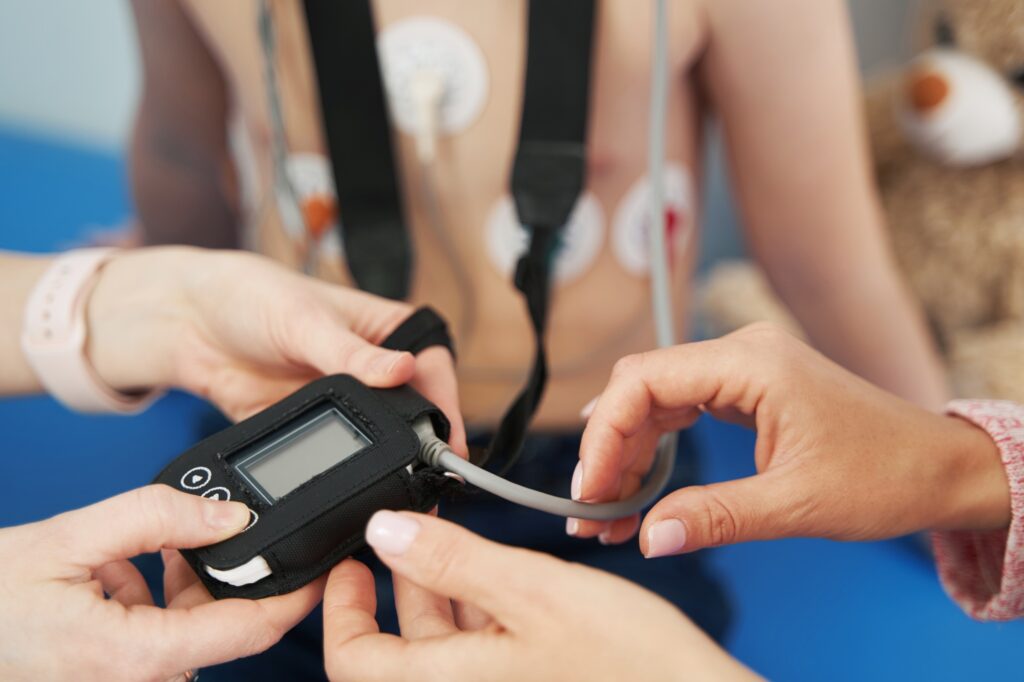
Purpose of the Holter Monitor
- Detect arrhythmias: Identify abnormal heart rhythms that may only occur intermittently, such as atrial fibrillation, ventricular tachycardia, or other types of arrhythmias.
- Assess unexplained symptoms: Evaluate heart activity when a patient experiences symptoms like dizziness, fainting, palpitations, or shortness of breath.
- Evaluate heart function: Track how the heart behaves during everyday activities, including physical exercise, stress, or sleep.
- Monitor treatment progress: For patients with heart rhythm issues, the monitor helps assess the effectiveness of treatments like medications, ablations, or pacemaker therapies.
How the Holter Monitor Works
Continuous Monitoring:
- The Holter Monitor continuously records the heart’s electrical activity, capturing every heartbeat. This provides a detailed and accurate record of any abnormalities, whether during normal activities, sleep, or exercise.
- Patients are encouraged to go about their daily routines as normal while the monitor records, ensuring the test captures heart activity under various conditions.


Benefits of Using a Holter Monitor
- Continuous Heart Monitoring: Provides a complete, uninterrupted record of the heart’s electrical activity over a longer period, helping detect problems that may not show up during a standard, short-duration ECG.
- Non-Invasive: The test is non-invasive and can be done outside of the hospital setting, allowing patients to go about their regular activities while being monitored.
- Accurate Diagnosis: The ability to capture heart rhythms throughout an entire day or longer helps doctors identify irregularities that might be missed during a single EKG.
- Symptom Correlation: By asking patients to keep a diary of their symptoms and activities, the Holter Monitor can correlate specific events with irregular heart rhythms, providing valuable insight into heart health.
Who Should Consider Using a Holter Monitor?
A Holter Monitor may be recommended for patients who:
- Experience irregular heartbeats, dizziness, fainting, or palpitations that are difficult to diagnose with a standard EKG.
- Have known arrhythmias or are being treated for heart rhythm problems and need continuous monitoring.
- Are recovering from a heart attack, surgery, or procedure and need follow-up evaluation.
- Require pacemaker or defibrillator monitoring to ensure the device is functioning properly.